 |
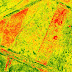
| NDVI Output Image |
What is NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index)?
Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) quantifies vegetation by measuring the difference between near-infrared (which vegetation strongly reflects) and red light (which vegetation absorbs).NDVI always ranges from -1 to +1. But there isn’t a distinct boundary for each type of land cover.
For example, when you have negative values, it’s highly likely that it’s water. On the other hand, if you have a NDVI value close to +1, there’s a high possibility that it’s dense green leaves.
But when NDVI is close to zero, there isn’t green leaves and it could even be an urbanized area.
How do you calculate NDVI?
As shown below, Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) uses the NIR and red channels in its formula.
Healthy vegetation (chlorophyll) reflects more near-infrared (NIR) and green light compared to other wavelengths. But it absorbs more red and blue light.
This is why our eyes see vegetation as the color green. If you could see near-infrared, then it would be strong for vegetation too. Satellite sensors like Landsat and Sentinel-2 both have the necessary bands with NIR and red.
 |
Image courtesy of NASA |
The result of this formula generates a value between -1 and +1. If you have low reflectance (or low values) in the red channel and high reflectance in the NIR channel, this will yield a high NDVI value. And vice versa.
Overall, NDVI is a standardized way to measure healthy vegetation. When you have high NDVI values, you have healthier vegetation. When you have low NDVI, you have less or no vegetation. Generally, if you want to see vegetation change over time, then you will have to perform atmospheric correction.
How do we use NDVI?
As mentioned before, satellites like Sentinel-2, Landsat and SPOT produce red and near infrared images.This GIS Dataset has data that you can download and create NDVI maps in ArcGIS or QGIS.
In particular, there are several sectors that use NDVI. For example, in agriculture, farmers use NDVI for precision farming and to measure biomass. Whereas, in forestry, foresters use NDVI to quantify forest supply and leaf area index.
Furthermore, NASA states that NDVI is a good indicator of drought. When water limits vegetation growth, it has a lower relative NDVI and density of vegetation.
In reality, there are hundreds of applications where NDVI and other remote sensing applicationsis being applied to in the real world.


0 comments:
Post a Comment